08. XHR's .send() method
To actually send the request, we need to use the send method:
asyncRequestObject.send();Let's check out what happens:
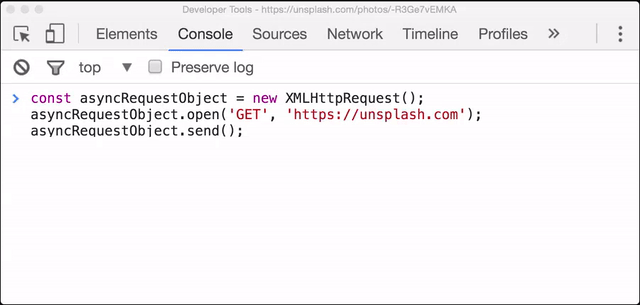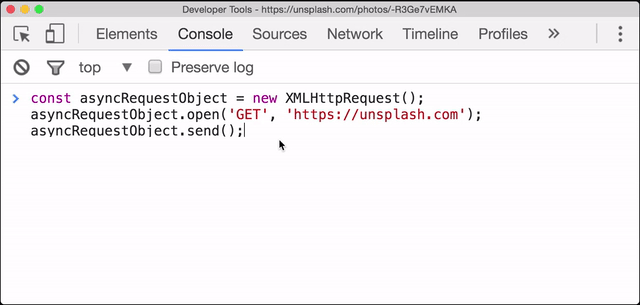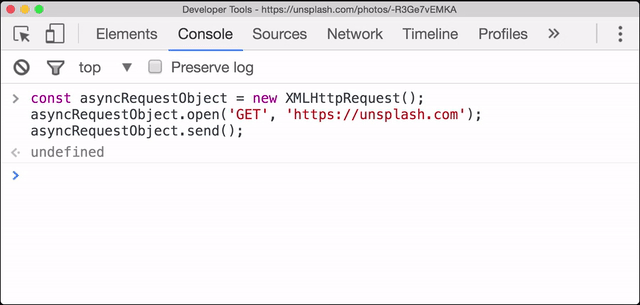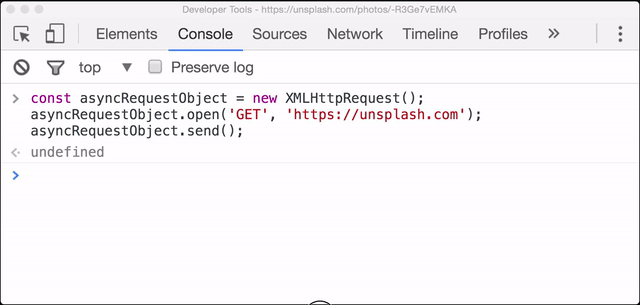
The XHR request is sent, but we don''t see anything!
XHR Request In Dev Tools
It's a little pointless to make a request for something but then do absolutely nothing with it! Why would you order some cake and then not go to pick it up or not eat it? The horror! We want to eat our cake, too!
Handling Success
To handle the successful response of an XHR request, we set the onload property on the object to a function that will handle it:
function handleSuccess () {
// in the function, the `this` value is the XHR object
// this.responseText holds the response from the server
console.log( this.responseText ); // the HTML of https://unsplash.com/
}
asyncRequestObject.onload = handleSuccess;As we just saw, if onload isn't set, then the request does return…but nothing happens with it.
Handling Errors
You might've picked up that onload is called when the response is successful. If something happens with the request and it can't be fulfilled, then we need to use the onerror property:
function handleError () {
// in the function, the `this` value is the XHR object
console.log( 'An error occurred 😞' );
}
asyncRequestObject.onerror = handleError;As with onload, if onerror isn't set and an error occurs, that error will just fail silently and your code (and your user!) won't have any idea what's wrong or any way to recover.